What actually is Industry 4.0:-
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, is the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT),
robotics, and automation into traditional manufacturing and industrial processes. Industry 4.0 aims to create a more efficient, flexible, and connected manufacturing system, allowing for increased productivity, improved quality, and better decision-making capabilities.
This new era of manufacturing involves the use of smart factories, where machines are able to communicate with each other and with humans in real time, making the entire production process more streamlined and responsive to changes in demand.
Industry 4.0 technologies also allow for more data collection and analysis, which can help manufacturers optimize their processes and identify opportunities for improvement.
Overall, Industry 4.0 represents a significant shift in the way we approach manufacturing and industrial processes and has the potential to drive major advances in productivity, efficiency, and innovation.
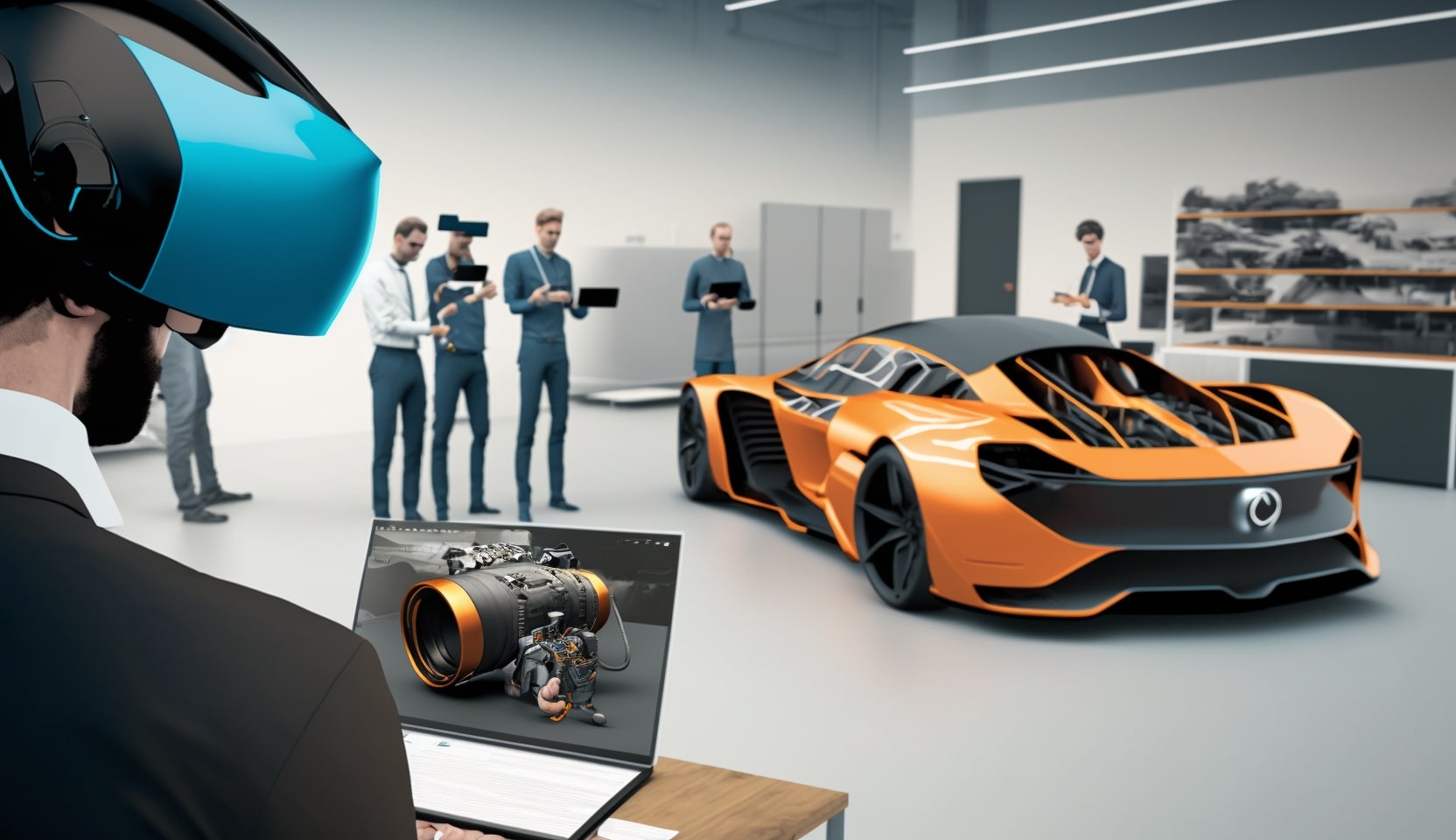
Virtual Reality(VR) has been transforming the way we experience gaming, entertainment, and education. But now, with Industry 4.0, VR is also transforming the manufacturing and industrial sectors.
VR technology is providing new ways for manufacturers to design, visualize, and test their products, while also improving worker safety and training.
Industry 4.0 represents a new era in manufacturing, characterized by the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and automation.
In this context, VR offers a unique set of capabilities that can be leveraged to drive innovation and enhance productivity.
“Virtual Reality for Formula One could be fantastic – driving the car!” –
Martin Sorrell Tweet
Applications of VR in Industry 4.0
One of the key applications of VR in Industry 4.0 is product design and visualization. VR allows manufacturers to create 3D models of their products and visualize them in a virtual environment, providing a more immersive and interactive experience than traditional 2D models.
This allows designers and engineers to test and refine their products in a simulated environment, identifying and addressing issues before they arise in the physical world.
In addition, VR can be used to create virtual prototypes, reducing the time and cost associated with physical prototyping.
With VR, manufacturers can create and test a virtually infinite number of design variations, enabling them to identify the most efficient and effective design solutions.
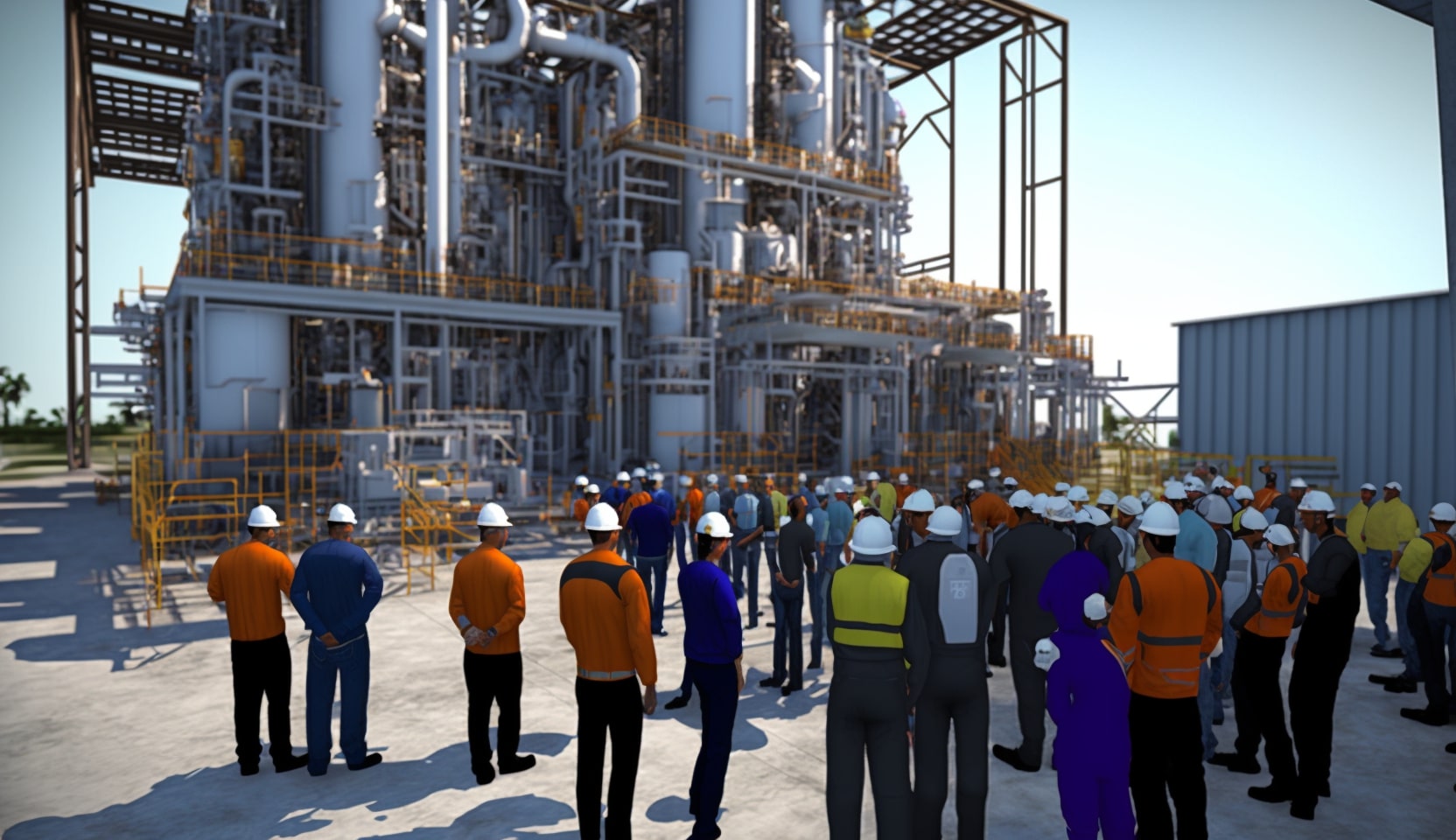
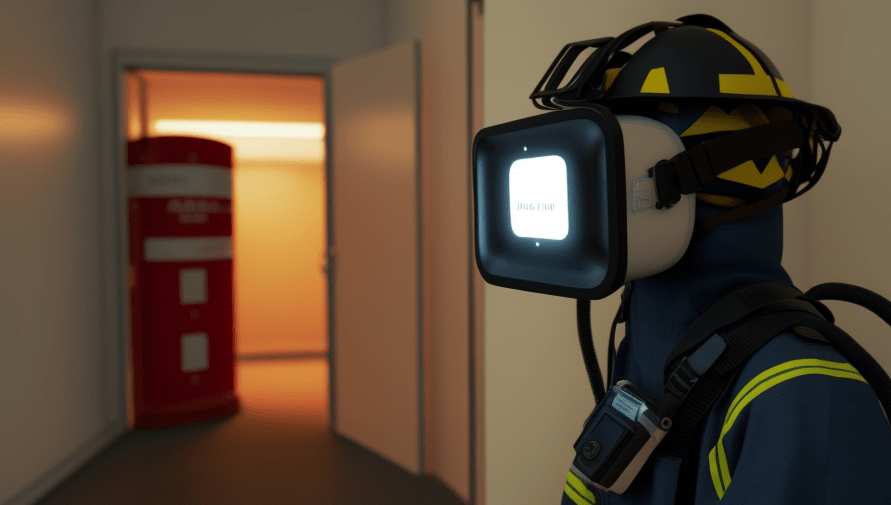
Another application of VR in Industry 4.0 is in training and education. VR provides a safe and controlled environment for workers to train on complex and dangerous equipment, reducing the risk of injury and improving learning outcomes.
VR also allows for more immersive and engaging training experiences, improving retention and comprehension.
Training in virtual reality has the potential to increase skill retention by 70% compared to conventional classroom-based training.
For more effective hands-on learning, businesses can construct virtual representations of locations to immerse their staff in. Professionals can develop their knowledge and motor skills in these settings without worrying about immediate dangers.
Explanation by real example:-
For example, imagine a worker who needs to learn how to operate a large piece of machinery. Instead of practicing on the real thing, which could be dangerous and potentially damaging to the equipment, the worker could practice in a virtual environment using a VR headset.
This would allow them to get a feel for the equipment and develop their skills in a safe and controlled environment.VR can also be used for remote training and collaboration, allowing workers to connect and communicate with colleagues and experts from anywhere in the world.
This is particularly useful in the current pandemic situation, where physical distancing and remote work have become the norm.
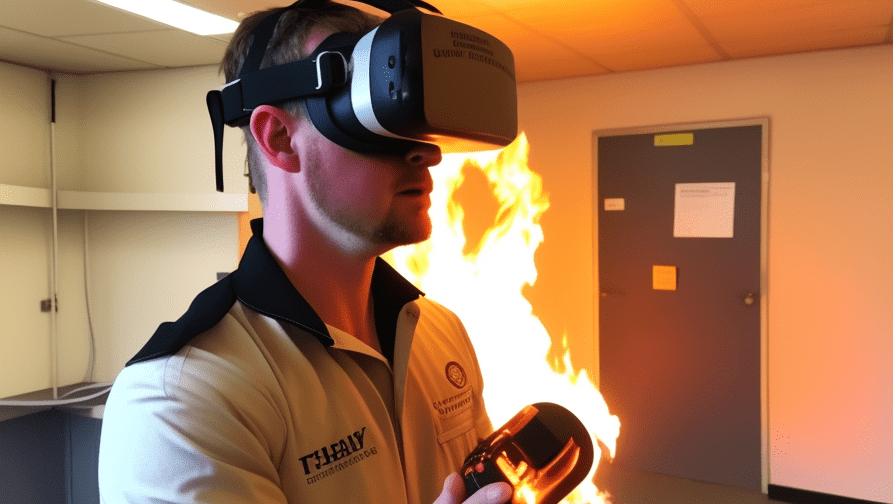
In addition, VR can be used to simulate and train for emergency situations, such as fires or other accidents.
This allows workers to develop their skills and preparedness in a realistic and immersive environment, improving their ability to respond effectively in the event of an actual emergency.
“There is some art that says the same thing to everybody. WE need something like that. What that is, I don’t know. But the virtual reality may be the key to it.”
– Jerry Garcia Tweet
ADVANTAGES OF VIRTUAL REALITY AND AUGMENTED REALITY IN INDUSTRY 4.0:
Finally, VR can be used to enhance worker safety in the manufacturing environment. By using VR, workers can be trained on safety procedures and protocols, such as the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) or how to safely operate machinery.
VR can also be used to identify potential safety hazards in the workplace, allowing manufacturers to proactively address and mitigate these risks.
- process development
- reduced downtime
- enhanced safety
- money saved

Conclusion:-
In conclusion, Virtual Reality is playing an increasingly important role in Industry 4.0, providing manufacturers with new capabilities and opportunities to innovate and improve productivity.
From product design and visualization to training and safety, VR is transforming the manufacturing and industrial sectors in exciting and innovative ways.
As the technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more applications of VR in Industry 4.0, driving further advancements and growth in these industries.















