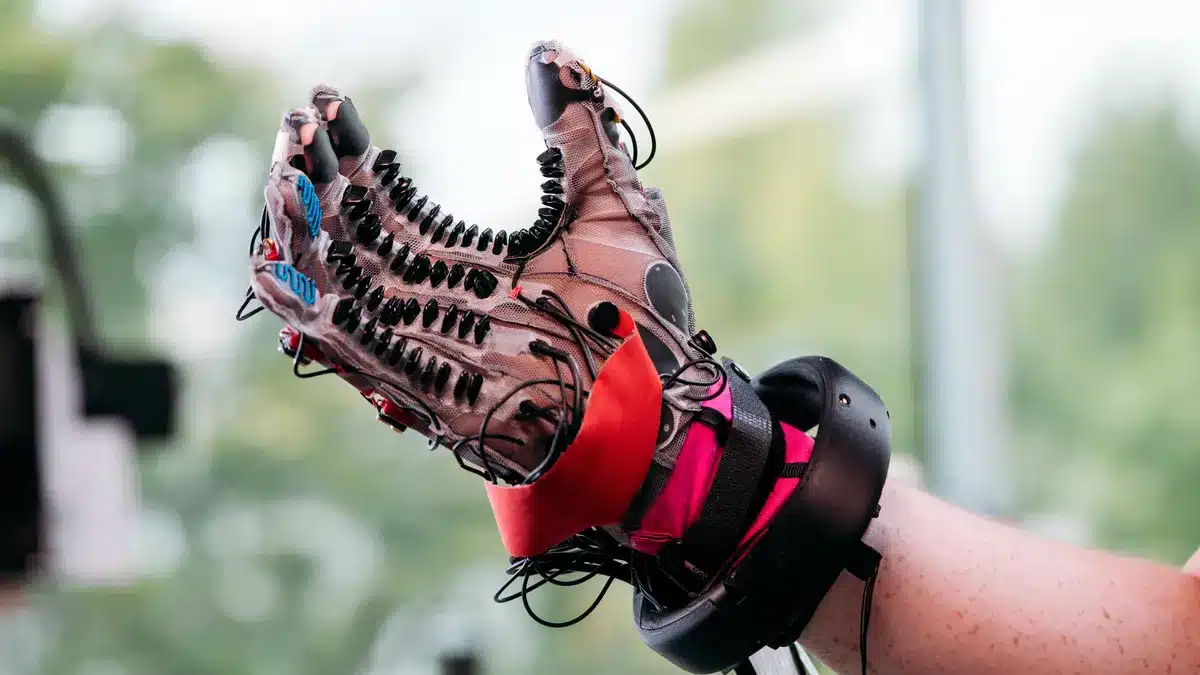
What if a robot could feel the world as richly as we do—with one continuous layer of smart skin? No bulky sensors, no mechanical complexity—just a soft, flexible surface that knows when it’s touched, pressed, scratched, or even bent.
That’s not sci-fi anymore.
Scientists at the University of Cambridge and University College London have created a single-layer e-skin that acts as a full-body sensor using just 32 electrodes and a brainy dose of machine learning. Their approach, published in Science Robotics, might just redefine how robots—and maybe even prosthetic limbs—“feel.”
Why This E-Skin Is a Game-Changer
Here’s what sets this breakthrough apart from previous e-skin technologies:
🔹 One Layer, Many Senses
Unlike traditional patchwork sensor arrays, this e-skin is made from a single hydrogel sheet embedded with 860,000 conductive pathways. That means no layering, no stitching, no need to glue different sensors together.
🔹 Full-Hand Awareness
The team shaped the hydrogel into a lifelike hand, then added 32 electrodes at the wrist. From that single entry point, they collected over 1.7 million data points, detecting:
- Pressure
- Cuts or physical damage
- Multi-point touches
- Joint bends
- Thermal changes
🔹 Smart, Not Complicated
Using electrical impedance tomography (EIT)—imagine sending gentle electrical pulses across the skin—they created full “touch maps.” Then, with AI models, they could classify six distinct kinds of tactile events, in real time.
What This Means for the Future
This technology has the potential to unlock the next generation of soft robotics, prosthetic limbs, wearables, and even smart clothing.
For robotics: Imagine humanoid robots that can “feel” if they’re gripping too tightly, or detect a soft pat on the back.
For prosthetics: Users could regain not just functionality—but actual, nuanced touch.
For manufacturing: Soft skins on robotic arms could spot anomalies in fragile or irregular materials.
Even better? This skin is cheap to make, recyclable, and custom-moldable—a far cry from traditional multi-layer electronic fabrication.
Why You Should Keep an Eye on This
Whether you’re into robotics, AI, biomedical engineering, or future tech in general—this is one of those developments that quietly but profoundly shifts what’s possible.
You can read the full article here:
🔗 Science Robotics DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.adq2303
Want to explore more futuristic tech? Check out:
Final Takeaway
The future of touch-sensitive robotics may not lie in complexity—but in elegant simplicity fused with intelligence. A single sheet of hydrogel, trained with AI, could soon give machines something close to the human sense of touch.